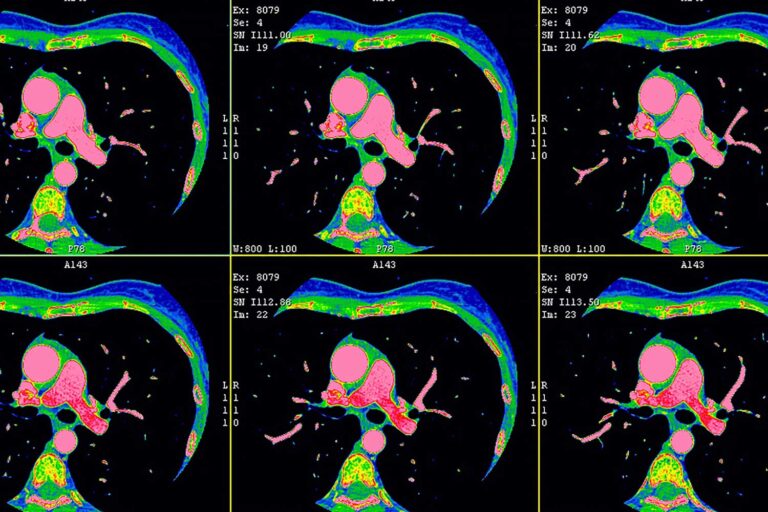
At Independent Physicians Medical Center (IPMC) in Northeast Philadelphia, we provide advanced imaging services to support the detection and evaluation of strokes in an accessible outpatient setting.
What Types of Tests Detect a Stroke?
Doctors use several tools to confirm a stroke and determine its cause. While physical exams and symptom evaluation are important, imaging tests provide the most definitive evidence of a stroke.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
A CT scan uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the brain. It’s often the first imaging test ordered because it can quickly show whether bleeding has occurred in the brain—a sign of a hemorrhagic stroke.
CT scans can also detect large areas of tissue damage from an ischemic stroke (caused by a blocked artery), though early ischemic changes may not be visible immediately. Doctors may also use specialized CT tests like CT angiography (CTA) to look closely at blood vessels in the head and neck.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
An MRI scan uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce highly detailed images of the brain. It’s often more sensitive than CT for detecting small or early ischemic strokes, especially when using advanced techniques like diffusion-weighted imaging.
MRI can show changes in brain tissue that might not be visible on a CT scan, making it especially useful for evaluating subtle strokes or assessing damage after symptoms have started.
How Imaging Helps Your Doctor
Imaging tests do more than confirm whether a stroke occurred. They help your physician:
- Differentiate stroke types — Is it ischemic (clot) or hemorrhagic (bleeding)?
- Locate the injured area of the brain
- Guide treatment decisions — Some treatments are effective only for certain stroke types.
- Assess blood flow and vessel health — Using CTA or other vascular imaging can detect narrowed or blocked arteries.
Other diagnostic tools—like carotid ultrasound, which evaluates blood flow in neck arteries—can help assess stroke risk and guide preventive care, although they don’t by themselves confirm a stroke.
Why Fast Imaging Matters
Stroke is a medical emergency. The sooner imaging can confirm what’s happening in the brain, the sooner treatment can begin. Early intervention can limit brain damage and improve long-term recovery outcomes.
IPMC Radiology
Stroke Imaging at IPMC in Northeast Philadelphia?
Convenient Location and Flexible Hours
Fast Appointments & Quick Results
Comfortable Outpatient Setting
Avoid the stress of a hospital visit. Our welcoming center is designed for efficiency and patient comfort
Experienced, Board-Certified Physicians
Your imaging is reviewed by experienced professionals dedicated to accuracy and personalized care.
Take Action if You Suspect a Stroke
Time is brain. If you or someone else shows signs of a stroke—such as sudden weakness, confusion, or trouble speaking—call 911 immediately. Early medical evaluation and imaging can be life-saving. For non-emergency imaging appointments after a referral, contact IPMC:
- 215-464-3300 to schedule.
- 9908 E. Roosevelt Blvd., Philadelphia, PA 19115
At Independent Physicians Medical Center, advanced imaging and compassionate care help you get answers and peace of mind when it matters most.